-

- Sopto Home
-

- Special Topic
-

- Module Knowledge
-

- How do Fiber optic transceivers work?
Module Knowledge
- Tips for Buying 10G XFP Transceivers
- XFP Transceivers for Telecommunications
- Three Types of Ethernet SFP Transceiver Modules Introduction
- Info about High Density CXP Optical Module
- Multipurpose CFP Optical Modules
- Info about CFP Management Interface
- SFP+ Transceivers Short Range Module Overview
- 3 Reasons Every Network Needs GLC-LH-SM Transceiver
- Is the GLC-SX-MM Transceiver Right for Your Switch?
SOPTO Special Topic
Certificate



Guarantee
Except products belongs to Bargain Shop section, all products are warranted by SOPTO only to purchasers for resale or for use in business or original equipment manufacturer, against defects in workmanship or materials under normal use (consumables, normal tear and wear excluded) for one year after date of purchase from SOPTO, unless otherwise stated...
Return Policies
Defective products will be accepted for exchange, at our discretion, within 14 days from receipt. Buyer might be requested to return the defective products to SOPTO for verification or authorized service location, as SOPTO designated, shipping costs prepaid. .....
Applications
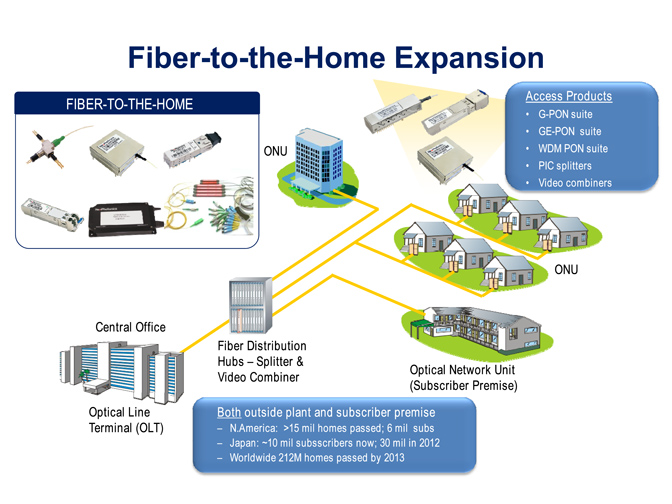 Fiber Optic Transceiver Modules can be applied to these occasions or fields.
Fiber Optic Transceiver Modules can be applied to these occasions or fields.
Ethernet
IPTV
FTTX
Security
Video Monitor
SDH/SONET
Data Communication
Storage Area Networks
SOPTO Products
- Fiber Optic Transceiver Module
- High Speed Cable
- Fiber Optical Cable
- Fiber Optical Patch Cords
- Splitter CWDM DWDM
- PON Solution
- FTTH Box ODF Closure
- PCI-E Network Card
- Network Cables
- Fiber Optical Adapter
- Fiber Optical Attenuator
- Fiber Media Converter
- PDH Multiplexers
- Protocol Converter
- Digital Video Multiplexer
- Fiber Optical Tools
- Compatible
Performance Feature
Stable
Low cost
Small size
Economic
Dust-proof
High speed
Hot-pluggable
Good EMI, EMC
Wide appliaction field
DDM function available
Long transmission distance
Good Anti-static performance
Module Knowledge
Recommended


How do Fiber optic transceivers work?
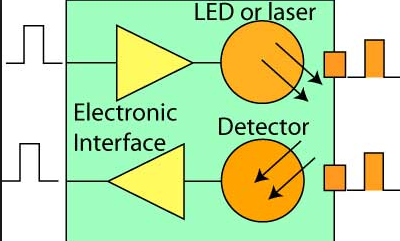
Fiber optic transceivers include both a transmitter and a receiver in the same component. These are arranged in parallel so that they can operate independently of each other. Both the receiver and the transmitter have their own circuitry so that they can handle transmissions in both directions.
Fiber optic transceivers can interface with two types of cables, single mode and multimode. Single mode is an optical fiber that will allow only one mode to propagate. The fiber has a very small core diameter of approximately 8 µm. It permits signal transmission at extremely high bandwidth and allows very long transmission distances. Multimode describes a fiber optic cable, which supports the propagation of multiple modes.
Multimode fiber may have a typical core diameter of 50 to 100 µm with a refractive index that is graded or stepped. It allows the use of inexpensive LED light sources and connector alignment and coupling is less critical than single mode fiber.
Distances of transmission and transmission bandwidth are less than with single mode fiber due to dispersion. Some fiber optic transceivers can be used for both single mode and multimode cables. Common connector types for fiber optic transceivers include Biconic, D4, ESCON, FC, FDDI, LC, Loopback, MTP, MT-RJ, MU, SC, SMA, and ST. General performance specifications to consider include wavelength, operating voltage, data rate, and bandwidth.
Important receiver performance parameters to consider when searching for fiber optic transceivers include sensitivity, responsivity, and receiver rise time. The sensitivity specifies the weakest optical signal that can be received. The minimum signal that can be received depends on the noise floor of the transceiver front end. The measure of responsivity is the ratio of radiant energy expressed in watts (W) incident on the device, to the resulting photocurrent expressed in amperes (A). It is represented as an absolute sensitivity expressed by A/W.
In the approximation of a step function, the receiver rise time is the time required for a signal to change from a specified 10% to 90% of full power. Rise time is a way of expressing the speed of the receiver. Important transmitter performance specifications to consider include light source, spectral width, and maximum optical output power and transmitter rise time.
>
The light source can be LED or laser diode. Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) have relatively large emitting areas and as a result are not as good light sources as Laser diodes. However, they are widely used for short to moderate transmission distances because they are much more economical. Laser Diodes (LDs) can couple many times more power to optical fiber than LEDs.
They are primarily used for applications that require the transmission of signals over long distances. In the approximation of a step function, the transmitter rise time is the time required for a signal to change from a specified 10% to 90% of full power. Rise time is a way of expressing the speed of the transmitter.
Common features for fiber optic transceivers include clock recovery, pigtail, stand alone, and signal input and output choices. An important environmental parameter to consider is the operating temperature.
Related Knowledge:
Guess Products You May Like:
 |  |  |  |
| 10G 1260~1620nm 40km CWDM X2 ER Transceiver Module | 10/100/1000M 100m Copper SFP Fiber Optic Transceiver | 1000BASE-T Copper GBIC Transceiver | 1.25g 1310/1490nm 20km CSFP Fiber Optic Transceiver Module |