-

- Sopto Home
-

- Special Topic
-

- Module Knowledge
-

- Fibre Channel over Ethernet will Change Architectures
Module Knowledge
- Tips for Buying 10G XFP Transceivers
- XFP Transceivers for Telecommunications
- Three Types of Ethernet SFP Transceiver Modules Introduction
- Info about High Density CXP Optical Module
- Multipurpose CFP Optical Modules
- Info about CFP Management Interface
- SFP+ Transceivers Short Range Module Overview
- 3 Reasons Every Network Needs GLC-LH-SM Transceiver
- Is the GLC-SX-MM Transceiver Right for Your Switch?
SOPTO Special Topic
Certificate



Guarantee
Except products belongs to Bargain Shop section, all products are warranted by SOPTO only to purchasers for resale or for use in business or original equipment manufacturer, against defects in workmanship or materials under normal use (consumables, normal tear and wear excluded) for one year after date of purchase from SOPTO, unless otherwise stated...
Return Policies
Defective products will be accepted for exchange, at our discretion, within 14 days from receipt. Buyer might be requested to return the defective products to SOPTO for verification or authorized service location, as SOPTO designated, shipping costs prepaid. .....
Applications
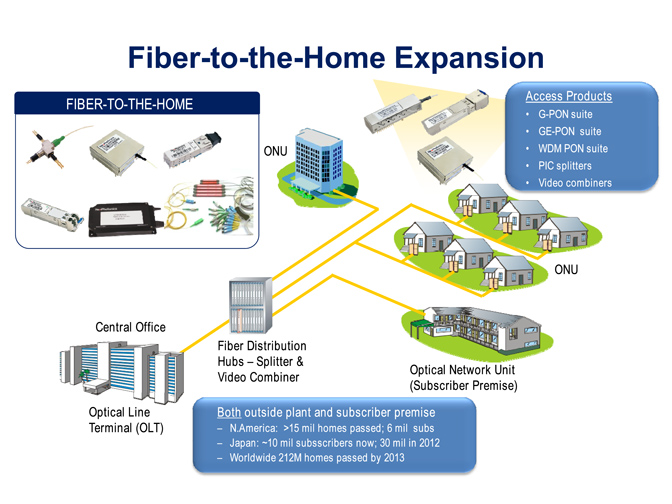 Fiber Optic Transceiver Modules can be applied to these occasions or fields.
Fiber Optic Transceiver Modules can be applied to these occasions or fields.
Ethernet
IPTV
FTTX
Security
Video Monitor
SDH/SONET
Data Communication
Storage Area Networks
SOPTO Products
- Fiber Optic Transceiver Module
- High Speed Cable
- Fiber Optical Cable
- Fiber Optical Patch Cords
- Splitter CWDM DWDM
- PON Solution
- FTTH Box ODF Closure
- PCI-E Network Card
- Network Cables
- Fiber Optical Adapter
- Fiber Optical Attenuator
- Fiber Media Converter
- PDH Multiplexers
- Protocol Converter
- Digital Video Multiplexer
- Fiber Optical Tools
- Compatible
Performance Feature
Stable
Low cost
Small size
Economic
Dust-proof
High speed
Hot-pluggable
Good EMI, EMC
Wide appliaction field
DDM function available
Long transmission distance
Good Anti-static performance
Module Knowledge
Recommended


Fibre Channel over Ethernet will Change Architectures
The transmission method, which encapsulates Fibre Channel frames into Ethernet frames, holds the promise of a unified-fabric solution.
Data centers use multiple networks that present operational and maintenance issues, as each network requires dedicated electronics and cabling infrastructure. Ethernet and Fibre Channel are the typical networks, with Ethernet providing a LAN between users and computing infrastructure, while Fibre Channel provides connections between servers and storage to create a storage area network (SAN).
Fibre Channel is T11 technical committee and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Data Center Bridging committee are defining standards to converge the two fabrics into a uni- fied fabric, with Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE).
What is FCoE?
FCoE is simply a transmission method in which the Fibre Channel frame is encapsulated into an Ethernet frame at the server. The server encapsulates Fibre Channel frames into Ethernet frames before sending them over the LAN, and de-encapsulates them when FCoE frames are received. Server input/output (I/O) consolidation combines the network interface card (NIC) and host bus adapter (HBA) cards into a single converged network adapter (CNA), which reduces server cabling and power/cooling needs.
.png)
Typical Infrastructure vs. First Generation FCoE
At present, the Ethernet frame is removed at the Ethernet edge switch to access the Fibre Channel frame, which is then transported to the SAN. Fibre Channel encapsulation requires use of 10-Gigabit Ethernet transmission electronics, as well as provides for increased server-to-SAN connectivity. FCoE encapsulation standards activity takes place at the Fibre Channel T11.3 committee.
Fibre Channel is a deterministic protocol that guarantees delivery of information. Native Ethernet has not been deterministic and has relied on transmission control protocol (TCP) to re-transmit dropped frames. With FCoE, the Ethernet transport has been required to be updated to ensure that frames/packets are lossless without using TCP/IP protocol. The new enhanced Ethernet standard is called Converged Enhanced Ethernet (CEE). CEE standards activity takes place at the IEEE 802.1 Data Center Bridging working groups.
FCoE cabling architectures
Typical data center cabling infrastructure now includes an Ethernet optical-fiber uplink to the access switches located at the server rack. Copper unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cables then interconnect to the server NIC. Fibre Channel frames are transmitted from the server HBA to the SAN using optical fiber. Laser-optimized 50-μm multimode fiber (OM3) is the default type of optical fiber used for Ethernet and Fibre Channel transport. Category 6 or Category 5 are typical copper UTP cables for edge-switch-to-server interconnect.
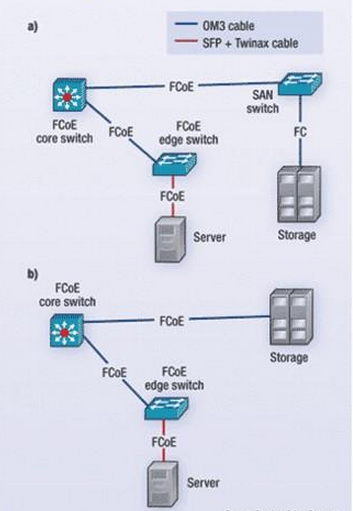
Second and Third Generation FCoE
First-generation FCoE implementation will focus on the edge switch and server. Ethernet OM3 optical uplinks will be received into the FCoE-enabled edge switch and then interconnected to the server CNA. Instead of copper UTP interconnects, small-form-factor pluggable + (SFP+) direct attached twinaxial copper cable is now used as the medium with significantly lower power and latency performance. The twinax copper cable will be used for distances up to 7 to 10 meters. Beyond that distance, low-cost, ultra-short reach (USR) SFP+ modules and OM3 optical fiber will be used.
The encapsulated Fibre Channel frame is returned to the edge switch where the Ethernet frame is removed to access the Fibre Channel frame. The Fibre Channel frame is then transmitted to the SAN. This architecture solution reduces the server interconnect cabling and adapter card number by at least 50%.
Second-generation FCoE deployments are expected to use FCoE-enabled core switches and edge switches. This architecture will continue to use basic Ethernet optical uplinks from the core switch to the edge switch and SFP+ twinax interconnects into the server. The difference occurs when the FCoE frame is transmitted back through the edge switch to the core switch over the same optical fiber previously used as the uplink to the server.
At the core switch, the FCoE frame is forwarded to the SAN director, where the Ethernet frame is removed and the Fibre Channel frame is then transmitted to the storage devices. This architecture solution reduces the server interconnect cabling and adapter card number by at least 50% and eliminates the Fibre Channel HBA-to-SAN optical- fiber trunk cable.
Third-generation FCoE architecture mirrors the second generation, with the exception that the core switch now forwards the FCoE frame directly to storage, where the Fibre Channel frame is accessed. This architecture solution reduces the server interconnect cabling and adapter card number by at least 50%, eliminates the Fibre Channel HBA-to-SAN optical-fiber trunk cable, and eliminates the core switch-to-SAN director fiber trunk cable.
The FCIA had adopted specific guidance relative to the cabling physical layer. Optical connectivity shall be in accordance with IEEE 802.3ae (10GBase-SR) using OM3 optical fiber. Additionally, the guidance recommends new installs to be =100 meters to be compatible with emerging 40/100-Gbit Ethernet installs and 16/32-Gbit Fibre Channel. SFP+ is the preferred connector for copper and optical cable. This eliminates the use of 10GBase-T copper UTP/shielded twisted-pair cable.
FCoE offers a data center unified-fabric solution that simplifies operational and maintenance of the cabling infrastructure. FCoE facilitates use of low-cost Ethernet electronics and OM3 optical connectivity to support 10-, 40, and 100-Gbit data rates.
For more info, please browse our website. For purchasing more fiber optical transceivers and other Fibre Channel Application Products, please contact a Sopto representative by calling 86-755-36946668, or by sending an email to info@sopto.com.
You May Like:




-180x180.JPG)




