-

- Sopto Home
-

- Special Topic
-

- Fiber Optics knowledge
-

- Fiber Optics’ Structure
Fiber Optics knowledge
- Maintained Methods of Fusion Splicer Parts
- How to Use the Fiber Optic Cleaver?
- What are Fixed Attenuators & Variable Attenuators?
- Deployable Fiber Optic Systems for Harsh Mining Environments
- Developing Miniature Fiber Optic Cable Has Become the Trend
- Fiber Optic Cleaning Procedures
- 6 Steps to Selecting a Fiber Optic Cable
- Signal Attenuation Introduction
- How Fiber Transmission Works?
SOPTO Special Topic
Certificate



Guarantee
Except products belongs to Bargain Shop section, all products are warranted by SOPTO only to purchasers for resale or for use in business or original equipment manufacturer, against defects in workmanship or materials under normal use (consumables, normal tear and wear excluded) for one year after date of purchase from SOPTO, unless otherwise stated...
Return Policies
Defective products will be accepted for exchange, at our discretion, within 14 days from receipt. Buyer might be requested to return the defective products to SOPTO for verification or authorized service location, as SOPTO designated, shipping costs prepaid. .....
Applications
Fiber Optis can be used in so many fields:
Data Storage Equipment
Interconnects,Networking
Gigabit Ethernet
FTTx, HDTV,CATV
Aerospace & Avionics
Data Transfer Tests
Network Equipment
Broadcast Automotive
Electronics,Sensing
Oil & Gas, Imaging
Outside Plant,Central Office
Harsh Environment
Data Transmission
Illumination,Institutions
Ship to Shore,Education
Simulation,Military,Space
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
Semiconductor Equipment
Diagnostics & Troubleshooting
Premise Networks Carrier Networks
Independent Telecommunication Providers
SOPTO Products
- Fiber Optic Transceiver Module
- High Speed Cable
- Fiber Optical Cable
- Fiber Optical Patch Cords
- Splitter CWDM DWDM
- PON Solution
- FTTH Box ODF Closure
- PCI-E Network Card
- Network Cables
- Fiber Optical Adapter
- Fiber Optical Attenuator
- Fiber Media Converter
- PDH Multiplexers
- Protocol Converter
- Digital Video Multiplexer
- Fiber Optical Tools
- Compatible
Performance Feature
Fiber Optics knowledge
Recommended


Fiber Optics’ Structure
The basic structure of an optical fiber consists of three parts; the core, the cladding, and the coating or buffer. The basic structure of an optical fiber is shown in figure 1. The core is a cylindrical rod of dielectric material. Dielectric material conducts no electricity. Light propagates mainly along the core of the fiber. The core is generally made of glass. The core is described as having a radius of (a) and an index of refraction n1. The core is surrounded by a layer of material called the cladding. Even though light will propagate along the fiber core without the layer of cladding material, the cladding does perform some necessary functions.
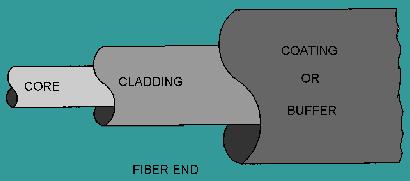
Figure1. - Basic structure of an optical fiber
The cladding layer is made of a dielectric material with an index of refraction n2. The index of refraction of the cladding material is less than that of the core material. The cladding is generally made of glass or plastic. The cladding performs the following functions:
- Reduces loss of light from the core into the surrounding air
- Reduces scattering loss at the surface of the core
- Protects the fiber from absorbing surface contaminants
- Adds mechanical strength
For extra protection, the cladding is enclosed in an additional layer called the coating or buffer. The coating or buffer is a layer of material used to protect an optical fiber from physical damage. The material used for a buffer is a type of plastic.
The buffer is elastic in nature and prevents abrasions. The buffer also prevents the optical fiber from scattering losses caused by microbends. Microbends occur when an optical fiber is placed on a rough and distorted surface.
For more high quality and low cost fiber optics, please contact SOPTO.
Related Knowledge:
How does Fiber Optic Cable Transmit Data?
What is Optical Fiber Composite Low-Voltage Cable?




-180x180.JPG)
