-

- Sopto Home
-

- Special Topic
-

- Module Knowledge
-

- Optical Module-What is Clock and Date Recovery?
Module Knowledge
- Tips for Buying 10G XFP Transceivers
- XFP Transceivers for Telecommunications
- Three Types of Ethernet SFP Transceiver Modules Introduction
- Info about High Density CXP Optical Module
- Multipurpose CFP Optical Modules
- Info about CFP Management Interface
- SFP+ Transceivers Short Range Module Overview
- 3 Reasons Every Network Needs GLC-LH-SM Transceiver
- Is the GLC-SX-MM Transceiver Right for Your Switch?
SOPTO Special Topic
Certificate



Guarantee
Except products belongs to Bargain Shop section, all products are warranted by SOPTO only to purchasers for resale or for use in business or original equipment manufacturer, against defects in workmanship or materials under normal use (consumables, normal tear and wear excluded) for one year after date of purchase from SOPTO, unless otherwise stated...
Return Policies
Defective products will be accepted for exchange, at our discretion, within 14 days from receipt. Buyer might be requested to return the defective products to SOPTO for verification or authorized service location, as SOPTO designated, shipping costs prepaid. .....
Applications
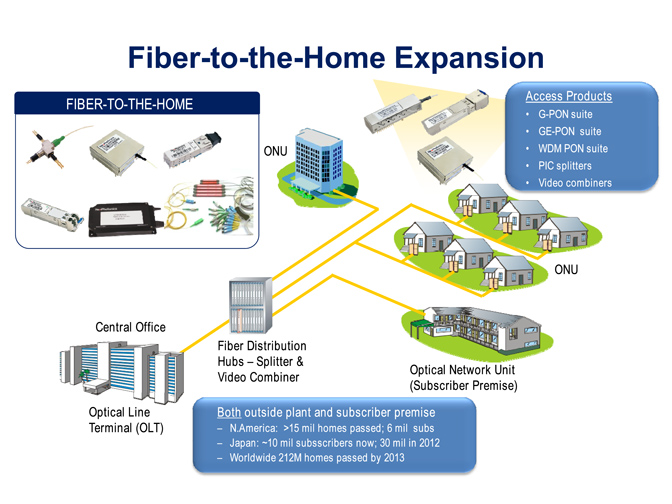 Fiber Optic Transceiver Modules can be applied to these occasions or fields.
Fiber Optic Transceiver Modules can be applied to these occasions or fields.
Ethernet
IPTV
FTTX
Security
Video Monitor
SDH/SONET
Data Communication
Storage Area Networks
SOPTO Products
- Fiber Optic Transceiver Module
- High Speed Cable
- Fiber Optical Cable
- Fiber Optical Patch Cords
- Splitter CWDM DWDM
- PON Solution
- FTTH Box ODF Closure
- PCI-E Network Card
- Network Cables
- Fiber Optical Adapter
- Fiber Optical Attenuator
- Fiber Media Converter
- PDH Multiplexers
- Protocol Converter
- Digital Video Multiplexer
- Fiber Optical Tools
- Compatible
Performance Feature
Stable
Low cost
Small size
Economic
Dust-proof
High speed
Hot-pluggable
Good EMI, EMC
Wide appliaction field
DDM function available
Long transmission distance
Good Anti-static performance
Module Knowledge
Recommended


What is Clock and Date Recovery?
Some digital data streams, especially high-speed serial data streams (such as the raw stream of data from the magnetic head of a disk drive) are sent without an accompanying clock signal. The receiver generates a clock from an approximate frequency reference, and then phase-aligns to the transitions in the data stream with a phase-locked loop (PLL). This process is commonly known as clock and data recovery (CDR). It is very closely related to the problem of carrier recovery, which is the process of re-creating a phase-locked version of the carrier when a suppressed carrier modulation scheme is used. These problems were first addressed in a 1956 paper, which introduced a clock recovery method now known as the Costas loop. Since then many additional methods have been developed.

In order for this scheme to work, a data stream must transition frequently enough to correct for any drift in the PLL's oscillator. The limit for how long a clock recovery unit can operate without a transition is known as its maximum consecutive identical digits (CID) specification. To ensure frequent transitions, some sort of encoding is used; 8B/10B encoding is very common, while Manchester encoding serves the same purpose in old revisions of 802.3 local area networks.
Related Knowledge:
Guess Products You May Like:
 |  |  |  |
| 6.25G 1310nm 2km SFP+ Fiber Optic Module | 10G 1260~1620nm 80km CWDM SFP+ Fiber Optic Transceiver Module | 10G 80KM DWDM SFP+ Optical Transceiver Module | 10G 1330nm 10km WDM BIDI XFP Optic Transceiver Module |