-

- Sopto Home
-

- Special Topic
-

- Fiber Optics knowledge
-

- BiDirectional Testing of Fiber Optic Cabling
Fiber Optics knowledge
- Maintained Methods of Fusion Splicer Parts
- How to Use the Fiber Optic Cleaver?
- What are Fixed Attenuators & Variable Attenuators?
- Deployable Fiber Optic Systems for Harsh Mining Environments
- Developing Miniature Fiber Optic Cable Has Become the Trend
- Fiber Optic Cleaning Procedures
- 6 Steps to Selecting a Fiber Optic Cable
- Signal Attenuation Introduction
- How Fiber Transmission Works?
SOPTO Special Topic
Certificate



Guarantee
Except products belongs to Bargain Shop section, all products are warranted by SOPTO only to purchasers for resale or for use in business or original equipment manufacturer, against defects in workmanship or materials under normal use (consumables, normal tear and wear excluded) for one year after date of purchase from SOPTO, unless otherwise stated...
Return Policies
Defective products will be accepted for exchange, at our discretion, within 14 days from receipt. Buyer might be requested to return the defective products to SOPTO for verification or authorized service location, as SOPTO designated, shipping costs prepaid. .....
Applications
Fiber Optis can be used in so many fields:
Data Storage Equipment
Interconnects,Networking
Gigabit Ethernet
FTTx, HDTV,CATV
Aerospace & Avionics
Data Transfer Tests
Network Equipment
Broadcast Automotive
Electronics,Sensing
Oil & Gas, Imaging
Outside Plant,Central Office
Harsh Environment
Data Transmission
Illumination,Institutions
Ship to Shore,Education
Simulation,Military,Space
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
Semiconductor Equipment
Diagnostics & Troubleshooting
Premise Networks Carrier Networks
Independent Telecommunication Providers
SOPTO Products
- Fiber Optic Transceiver Module
- High Speed Cable
- Fiber Optical Cable
- Fiber Optical Patch Cords
- Splitter CWDM DWDM
- PON Solution
- FTTH Box ODF Closure
- PCI-E Network Card
- Network Cables
- Fiber Optical Adapter
- Fiber Optical Attenuator
- Fiber Media Converter
- PDH Multiplexers
- Protocol Converter
- Digital Video Multiplexer
- Fiber Optical Tools
- Compatible
Performance Feature
Fiber Optics knowledge
Recommended


BiDirectional Testing of Fiber Optic Cabling
Bi-directional testing of fiber optic cable is important to insure the quality of a fiber network. The main reason for this is due to the fact that no two glass fibers are exactly same. Whether the fiber optic cables are manufactured by different companies or they happened to come off another reel, their fibers may have slightly different core sizes due to core-cladding concentricity mismatches.
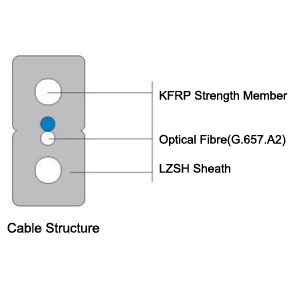
Self-Supporting Drop Optical Cable
For example, if the transmitting light travels from a larger core to a slightly smaller one or if the cores are offset during the fusion splice or connection process, you will witness more attenuation in one direction than the other. Therefore, it is essential to measure both directions. Once you have gathered the bi-directional measurements you calculate the average which is known as the ‘average link loss.’ Using the bi-directional average enables networkers to adequately measure splice loss.
Generally, network operators use optical time domain reflectometers (OTDR) to determine loss. Simply, the OTDR sends light through the fiber and then measures the amount that is reflected back, as well as how much time it took. In addition to attenuation, these meters have the ability to locate breaks in fiber, splices and connectors and reflection properties at multiple wavelengths.
For more info, please browse our website.




-180x180.JPG)