-

- Sopto Home
-

- Special Topic
-

- Fiber Optics knowledge
-

- The Difference between Loose Tube Fiber and Tight Buffer Fiber
Fiber Optics knowledge
- Maintained Methods of Fusion Splicer Parts
- How to Use the Fiber Optic Cleaver?
- What are Fixed Attenuators & Variable Attenuators?
- Deployable Fiber Optic Systems for Harsh Mining Environments
- Developing Miniature Fiber Optic Cable Has Become the Trend
- Fiber Optic Cleaning Procedures
- 6 Steps to Selecting a Fiber Optic Cable
- Signal Attenuation Introduction
- How Fiber Transmission Works?
SOPTO Special Topic
Certificate



Guarantee
Except products belongs to Bargain Shop section, all products are warranted by SOPTO only to purchasers for resale or for use in business or original equipment manufacturer, against defects in workmanship or materials under normal use (consumables, normal tear and wear excluded) for one year after date of purchase from SOPTO, unless otherwise stated...
Return Policies
Defective products will be accepted for exchange, at our discretion, within 14 days from receipt. Buyer might be requested to return the defective products to SOPTO for verification or authorized service location, as SOPTO designated, shipping costs prepaid. .....
Applications
Fiber Optis can be used in so many fields:
Data Storage Equipment
Interconnects,Networking
Gigabit Ethernet
FTTx, HDTV,CATV
Aerospace & Avionics
Data Transfer Tests
Network Equipment
Broadcast Automotive
Electronics,Sensing
Oil & Gas, Imaging
Outside Plant,Central Office
Harsh Environment
Data Transmission
Illumination,Institutions
Ship to Shore,Education
Simulation,Military,Space
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
Semiconductor Equipment
Diagnostics & Troubleshooting
Premise Networks Carrier Networks
Independent Telecommunication Providers
SOPTO Products
- Fiber Optic Transceiver Module
- High Speed Cable
- Fiber Optical Cable
- Fiber Optical Patch Cords
- Splitter CWDM DWDM
- PON Solution
- FTTH Box ODF Closure
- PCI-E Network Card
- Network Cables
- Fiber Optical Adapter
- Fiber Optical Attenuator
- Fiber Media Converter
- PDH Multiplexers
- Protocol Converter
- Digital Video Multiplexer
- Fiber Optical Tools
- Compatible
Performance Feature
Fiber Optics knowledge
Recommended


The Difference between Loose Tube Fiber and Tight Buffer Fiber
Tight-buffered cables often are used for intra-building, risers, general building and plenum applications. Tight buffer fiber contains a thick coating of a plastic-type material which is applied directly to the outside of each individual fiber.
Loose tube fiber optic cable is typically used for outside-plant installation in aerial, duct and direct-buried applications. Loose tube fiber contains multiple strands of fiber in a single jacket. Since the fibers are "loose" inside the jacket, outside forces are less likely to reach the fibers. This makes it the more durable option of the two.
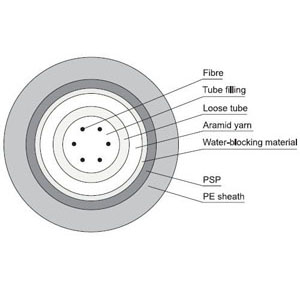
Loose Tube Cable
Loose-tube fiber generally consists of 12 strand of fiber, but can range anywhere as low as 6, all the way up to 244 strands. Loose tube cables can be either dielectric or optionally armored. The modular buffer-tube design permits easy drop-off groups of fibers at intermediate points, without interfering with other protected buffer tubes being routed to other locations. The loose tube design also helps in the identification and administration of fibers in the system.
In a loose tube cable design, color-coded plastic buffer tubes house and protect optical fibers. An optional gel filling compound impedes water penetration. Excess fiber length (relative to buffer tube length) insulates fibers from stresses of installation and environmental loading. Buffer tubes are stranded around a dielectric or steel central member, which serves as an anti-buckling element.
The cable core typically uses aramid yarn, as the primary tensile strength member. The outer polyethylene jacket is extruded over the core. If armoring is required, a corrugated steel tape is formed around a single jacketed cable with an additional jacket extruded over the armor.
Water-blocking Roader Cable with High Strength Loose Tube
Tight-Buffered Cable
Single fiber tight buffered cables are used as pigtails, optical patch cord or fiber jumpers to terminate loose tube cables directly into opto-electronic transmitters, receivers and other active and passive components. Multi fiber tight buffered cables also are available and are used primarily for alternative routing and handling flexibility and ease within buildings. With tight buffered cable designs, the buffering material is in direct contact with the fiber. This design is suited for "jumper cables" which connect outside plant cables to terminal equipment, and also for linking various devices in a premises network.
The tight-buffered design provides a rugged cable structure to protect individual fibers during handling, routing and connectorization. Yarn strength members keep the tensile load away from the fiber.
Compared with loose-tube cables, optical specifications for tight-buffered cables also should include the maximum performance of all fibers over the operating temperature range and life of the cable. Averages should not be acceptable.
Sopto supplies high quality fiber optics with reasonable price. For the newest quotes, please contact a Sopto representative by calling 86-755-36946668, or by sending an email to info@sopto.com. For more info, please browse our website.




-180x180.JPG)