-

- Sopto Home
-

- Special Topic
-

- Fiber Optics knowledge
-

- How to Make Water Fiber Optics?
Fiber Optics knowledge
- Maintained Methods of Fusion Splicer Parts
- How to Use the Fiber Optic Cleaver?
- What are Fixed Attenuators & Variable Attenuators?
- Deployable Fiber Optic Systems for Harsh Mining Environments
- Developing Miniature Fiber Optic Cable Has Become the Trend
- Fiber Optic Cleaning Procedures
- 6 Steps to Selecting a Fiber Optic Cable
- Signal Attenuation Introduction
- How Fiber Transmission Works?
SOPTO Special Topic
Certificate



Guarantee
Except products belongs to Bargain Shop section, all products are warranted by SOPTO only to purchasers for resale or for use in business or original equipment manufacturer, against defects in workmanship or materials under normal use (consumables, normal tear and wear excluded) for one year after date of purchase from SOPTO, unless otherwise stated...
Return Policies
Defective products will be accepted for exchange, at our discretion, within 14 days from receipt. Buyer might be requested to return the defective products to SOPTO for verification or authorized service location, as SOPTO designated, shipping costs prepaid. .....
Applications
Fiber Optis can be used in so many fields:
Data Storage Equipment
Interconnects,Networking
Gigabit Ethernet
FTTx, HDTV,CATV
Aerospace & Avionics
Data Transfer Tests
Network Equipment
Broadcast Automotive
Electronics,Sensing
Oil & Gas, Imaging
Outside Plant,Central Office
Harsh Environment
Data Transmission
Illumination,Institutions
Ship to Shore,Education
Simulation,Military,Space
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
Semiconductor Equipment
Diagnostics & Troubleshooting
Premise Networks Carrier Networks
Independent Telecommunication Providers
SOPTO Products
- Fiber Optic Transceiver Module
- High Speed Cable
- Fiber Optical Cable
- Fiber Optical Patch Cords
- Splitter CWDM DWDM
- PON Solution
- FTTH Box ODF Closure
- PCI-E Network Card
- Network Cables
- Fiber Optical Adapter
- Fiber Optical Attenuator
- Fiber Media Converter
- PDH Multiplexers
- Protocol Converter
- Digital Video Multiplexer
- Fiber Optical Tools
- Compatible
Performance Feature
Fiber Optics knowledge
Recommended


How to Make Water Fiber Optics?
To make water fiber optics, what you should need is “A Plastic Bottle”, “A Torch (Flashlight if you must)”, “A Source of Water” and something to make a hole in the plastic bottle.

Tools of making water fiber optics
Then, what to do? Follow the tips.
- Make a small round (~5mm) hole in the side of the bottle near the base. It is probably best to use a drill to do this as the bottle will be very slippery.
- Put your finger over the hole and fill the bottle up with water.
- Shine the torch through the bottle at the back of the hole
- Remove your finger from the hole and move it down the stream of water.
Then, what will be happened?
You should notice a spot of light on your hand while it is in the stream of water even though it must have gone around a corner to get there. It tends to work best when the water comes out quite slowly.

A spot of light on your hand
And, you may ask “Why does it happen?” Now, let’s show the truth.
To understand what is going on here it helps to do another experiment. Fill a transparent bowl with water, put something in the bowl and then look upwards at the bottom of water.

The bowl filled with water
To understand what is going on here it helps to do another experiment. Fill a transparent bowl with water, put something in the bowl and then look upwards at the bottom of water.
If you look at the bowl from the top you can see the spoon at the bottom.
Looking upwards in the bowl of water you see a reflection of the spoon at the bottom of the bowl in the surface. The water is behaving like a mirror.
So light will reflect really well off the inside surface of water at a relatively small angle.
This means that if you shine the light into a tube of water whenever it meets the side it is reflected so the light stays within the water until it hits your hand lighting it up. This happens even if the water goes around a corner.
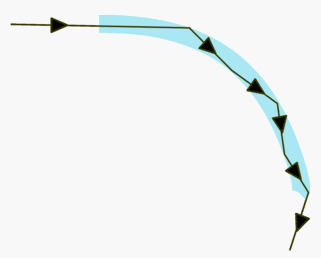
Light reflects in a tube of water
What has this got to do with fibre optics?
If instead of making the tube out of water you use very very pure glass and pull it to a thin flexible fibre, when you shine light in at one end it will come out of the other. By getting the right design of fibre the light can travel through up to 50km of fibre and still be detectable.
You can then send signals through the fibre by flashing the light on and off again a bit like morse code, because you can flash the light very fast you can transfer huge amounts of information. The record is now over 1000 GB per second down a single optical fibre.
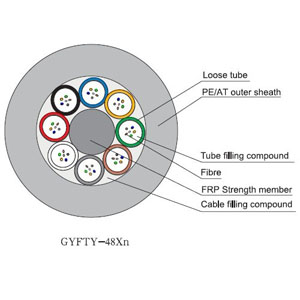
GYFTY Loose Tube Optical Cable
Because they are so good at transmitting data optic fibres move most of the data around the world (internet traffic, phone calls etc.) and you are almost certainly reading this via one.
If you make the tube out of plastic rather than glass it is more flexible and safer, and you can use it to make the artificial Christmas trees with the tiny pin pricks of light.
Light goes more slowly in water than in air and whenever light changes materials and the speed changes it will be bent (refracted). When it moves from a slow material (like water) to a faster one (like air) it is bent towards the surface.
Why do you get such a good reflection from the surface of the water?
Light goes more slowly in water than in air and whenever light changes materials and the speed changes it will be bent (refracted). When it moves from a slow material (like water) to a faster one (like air) it is bent towards the surface.
.png)
Light in water
If light leaves water at an angle it is refracted closer to the surface. Some light is reflected back into the water but not very much.
The smaller the angle the light meets the surface at, the bigger the change in angle.
At a certain point the refracted light should be inside the water. Light must leave the water to refract so this is impossible, so all the light is reflected. This is known as total internal reflection.
For more info, please browse our website. For purchasing more fiber optic assembly products, please contact a Sopto representative by calling 86-755-36946668, or by sending an email to info@sopto.com.




-180x180.JPG)