-

- Sopto Home
-

- Special Topic
-

- Fiber Optics knowledge
-

- Fiber Optics Classification
Fiber Optics knowledge
- Maintained Methods of Fusion Splicer Parts
- How to Use the Fiber Optic Cleaver?
- What are Fixed Attenuators & Variable Attenuators?
- Deployable Fiber Optic Systems for Harsh Mining Environments
- Developing Miniature Fiber Optic Cable Has Become the Trend
- Fiber Optic Cleaning Procedures
- 6 Steps to Selecting a Fiber Optic Cable
- Signal Attenuation Introduction
- How Fiber Transmission Works?
SOPTO Special Topic
Certificate



Guarantee
Except products belongs to Bargain Shop section, all products are warranted by SOPTO only to purchasers for resale or for use in business or original equipment manufacturer, against defects in workmanship or materials under normal use (consumables, normal tear and wear excluded) for one year after date of purchase from SOPTO, unless otherwise stated...
Return Policies
Defective products will be accepted for exchange, at our discretion, within 14 days from receipt. Buyer might be requested to return the defective products to SOPTO for verification or authorized service location, as SOPTO designated, shipping costs prepaid. .....
Applications
Fiber Optis can be used in so many fields:
Data Storage Equipment
Interconnects,Networking
Gigabit Ethernet
FTTx, HDTV,CATV
Aerospace & Avionics
Data Transfer Tests
Network Equipment
Broadcast Automotive
Electronics,Sensing
Oil & Gas, Imaging
Outside Plant,Central Office
Harsh Environment
Data Transmission
Illumination,Institutions
Ship to Shore,Education
Simulation,Military,Space
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
Semiconductor Equipment
Diagnostics & Troubleshooting
Premise Networks Carrier Networks
Independent Telecommunication Providers
SOPTO Products
- Fiber Optic Transceiver Module
- High Speed Cable
- Fiber Optical Cable
- Fiber Optical Patch Cords
- Splitter CWDM DWDM
- PON Solution
- FTTH Box ODF Closure
- PCI-E Network Card
- Network Cables
- Fiber Optical Adapter
- Fiber Optical Attenuator
- Fiber Media Converter
- PDH Multiplexers
- Protocol Converter
- Digital Video Multiplexer
- Fiber Optical Tools
- Compatible
Performance Feature
Fiber Optics knowledge
Recommended


Fiber Optics Classification
According to the classification standard of different optical fiber, a fiber will have different names.
According to the material of fiber
According to the optical fiber's materials, fiber optics can be divided into quartz fiber and plastic optical fiber.
Quartz optical fiber is generally composed of doped silica core and doped silica cladding. This fiber's dispersion loss is low and moderate. At present, quartz optical fiber is the most common communication optical fiber.
Plastic optical fiber is a new kind of fiber used in communication, is still in the development phase of the trial.
Plastic optical fiber has large loss, coarse core diameter (diameter of 100 ~ 600 μ m), large numerical aperture (NA) (generally 0.3 ~ 0.5) characteristics and lower manufacturing cost. At present, the application of plastic optical fiber is suitable for short length, such as indoor computer networking and communications of ship.
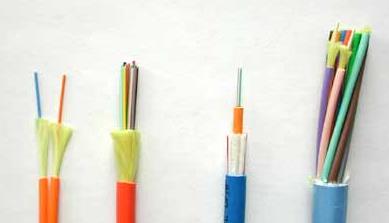
Optical Fiber Classification
According to the optical fiber refractive index profile
According to the optical fiber refractive index profile of different fiber types, can be divided into step type optical fiber and graded index optical fiber.
According to the transmission mode
According to modes of optical transmission, optical fiber can be divided into multimode optical fiber and single mode fiber.
Single mode fiber only can transmit one mode. Single mode optical fiber only can transmit basic mode (the lowest order mode), without time delay between mode.
Single mode provides much larger bandwidth than multi-mode fiber, which is very important for high code rate transmission.
The mode field diameter of single mode optical fiber is only a few microns (μ m), its bandwidth than the graded index multimode fiber bandwidth is one or two orders of magnitude higher. Therefore, it is applicable to the large capacity, long distance communication
According to the international classification standards (recommended classification according to ITU-T)
In order to make the fiber with uniform international standard, International Telecommunication Union (ITU-T) developed a fiber standard (G standard). According to the proposal of ITU-T, fiber optics can be divided into:
- G.651 fiber (50/125 μ m multimode graded index fiber)
- G.652 optical fiber (non dispersion shifted fiber)
- G.653 optical fiber (Dispersion shifted fiber DSF)
- G.654 optical fiber (cutoff wavelength shift fiber)
- G.655 optical fiber (non zero dispersion shift fiber)
In order to adapt to the development of new technology, the G.652 fiber has been further divided to G.652A, G.652B, G.652C three sub classes. G.655 fiber is also further divided into two subclasses of G.655A, G.655B.
Classification according to IEC standards, fiber optics is divided into:
Class A multimode fiber:
- A1a multimode fiber (50/125 μ m multimode fiber
- A1b multimode fiber (62.5/125 μ m multimode fiber
- A1d multimode fiber (100/140 μ m multimode fiber
Class B single mode optical fiber:
- B1.1 corresponds to the G652 fiber optics
- B1.3 correspond to the G652C fiber optics
- B1.2 corresponds to the G654 fiber optics
- B2 corresponds to the G.653 optical fiber
- B4 corresponds to the G.655 optical fiber
For more high quality and low cost fiber optics, please contact SOPTO.
Related Knowledge:
How does a fiber optic cable work?
What is a Fiber Optic Patch Panel?
FTTX Drop Cable Construction Methods
Quality Control in Optical Fiber Production
How to Fusion Splice a Fiber Optic Cable