-

- Sopto Home
-

- Special Topic
-

- Multiplexer Knowledge
-

- Outlook of the WDM Networks
Multiplexer Knowledge
- Why is Multiplexing Needed in Data Communication Systems?
- What is Concept of Multiplexing in Telephone System?
- What is Digital TV Frequency?
- Outlook of the WDM Networks
- DWDM Technical Overview
- CWDM Technical Overview
- How to Activate Cable Modems?
- How to Install a Fiber Optic Modem?
- How do I Choose a Best Fiber Modem?
SOPTO Special Topic
Certificate



Guarantee
Except products belongs to Bargain Shop section, all products are warranted by SOPTO only to purchasers for resale or for use in business or original equipment manufacturer, against defects in workmanship or materials under normal use (consumables, normal tear and wear excluded) for one year after date of purchase from SOPTO, unless otherwise stated...
Return Policies
Defective products will be accepted for exchange, at our discretion, within 14 days from receipt. Buyer might be requested to return the defective products to SOPTO for verification or authorized service location, as SOPTO designated, shipping costs prepaid. .....
Applications
Multiplexers can be used to connect PBX, Hot line and other devices of network from central site to user site through fiber optical cable.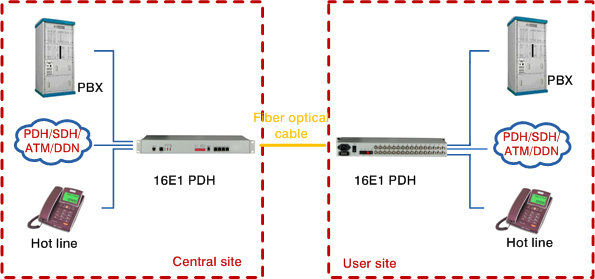
SOPTO Products
- Fiber Optic Transceiver Module
- High Speed Cable
- Fiber Optical Cable
- Fiber Optical Patch Cords
- Splitter CWDM DWDM
- PON Solution
- FTTH Box ODF Closure
- PCI-E Network Card
- Network Cables
- Fiber Optical Adapter
- Fiber Optical Attenuator
- Fiber Media Converter
- PDH Multiplexers
- Protocol Converter
- Digital Video Multiplexer
- Fiber Optical Tools
- Compatible
Related Products
Performance Feature
High integration desig
Low power consumption
Good EMC, EMI
Stable and Reliable
Multiplexer Knowledge
Recommended


Outlook of the WDM Networks
The throughput in optical networks is increasing inexorably, the backhauling traffic generated by triple-play and video-on-demand services being the main drivers. Therefore, the very first application for 100G systems for Ethernet transport is anticipated in metro networks and storage-area networks. A serial transmission approach is effective in the case of large capacities that require WDM transmission, because of the reduced efforts for wavelength management.
However, the way 100GbE transponders will be realized depends on the network environment. What’s needed for 100GbE transport is different for point-to-point connections, meshed networks, or meshed networks with ROADMs. For meshed networks, the transmission reach is critical due to the PMD of the fibers forming that network. In meshed networks with ROADMs, the signal, in addition must have a high robustness against narrowband filtering brought on by cascaded ROADMs.
In a WDM network the commonly used frequency grid is either 50 or 100 GHz, which will have a major effect on which from the above-described approaches can be applied. Also a mixed bit rate operation with 10 or 40 Gbps channels and 100 Gbps channels must be studied.
Of course, 100GbE can invariably be realized with a WDM approach (e.g., 10×10 Gbps), but this will not increase the actual throughput. Such a WDM approach could be attractive for low-cost application, but for networks with dimensions of a MAN or WAN the wavelength management effort could be complex. For instance, if we assume a guy with ROADMs in case of a WDM approach several channels need to be dropped at a time instead of a single channel. We accept that the serial processes for realizing a 100GbE will mainly be suitable for MAN a WAN. If so such 100GbE transmission systems have to full-fill several other requirements of carriers.
Ethernet has in principle the reputation of being a low-cost technology. Besides the advantages of serial approach, the serial approaches will have to compete with WDM approaches regarding the cost for the terminal equipment. This possible only when components are matured and integration is progressing indicated in the chapter on components for 100G systems.
For more info, please browse our website.




