-

- Sopto Home
-

- Special Topic
-

- FTTH Knowledge
-

- Advantages of distribution cabling in FTTH
FTTH Knowledge
- Solving the FTTH Rollout Problem in Multiple Dwelling Units
- WDM PON Introduction FAQ
- A Simple Overview of Optical Power Meter
- ODN is based on PON FTTH Optical Cable Network of the Device
- Using an OTDR to be an Expert in Fiber Link Testing
- How FTTH Broadband Works?
- Connections among Fiber Terminal Boxes & Patch Cables & Pigtails
- Easy to Install a Fiber Terminal Box
- What is Arrayed Waveguide Grating?
SOPTO Special Topic
Certificate



Guarantee
Except products belongs to Bargain Shop section, all products are warranted by SOPTO only to purchasers for resale or for use in business or original equipment manufacturer, against defects in workmanship or materials under normal use (consumables, normal tear and wear excluded) for one year after date of purchase from SOPTO, unless otherwise stated...
Return Policies
Defective products will be accepted for exchange, at our discretion, within 14 days from receipt. Buyer might be requested to return the defective products to SOPTO for verification or authorized service location, as SOPTO designated, shipping costs prepaid. .....
Applications

Sopto supply the best FTTH solutions for your network!
SOPTO Products
- Fiber Optic Transceiver Module
- High Speed Cable
- Fiber Optical Cable
- Fiber Optical Patch Cords
- Splitter CWDM DWDM
- PON Solution
- FTTH Box ODF Closure
- PCI-E Network Card
- Network Cables
- Fiber Optical Adapter
- Fiber Optical Attenuator
- Fiber Media Converter
- PDH Multiplexers
- Protocol Converter
- Digital Video Multiplexer
- Fiber Optical Tools
- Compatible
Related Products
Performance Feature
FTTH Knowledge
Recommended

Advantages of distribution cabling in FTTH
The “Distribution Cabling” runs from the FCP further into the FTTH network and closer to the subscriber base.
Distribution cabling may only need to cover distances of less than 1km before final breakout to the subscribers.
Distribution cabling will generally consist of medium-sized fibre counts targeted to serve a specific number of buildings within the FTTH area.
For underground networks, distribution cables may be ducted, direct buried or grouped within a common micro-duct or tubing network to minimize construction costs and allow other cables to be added on a ‘grow as you go’ basis.
For larger Main Distribution Units (MDUs), the distribution cabling may form the last drop to the building and convert to internal cabling to complete the fibre link. For aerial networks the arrangement will be similar to that of feeder cables.
Distribution cables are smaller in size than the feeder cables. Fibre counts will generally be 48-192.
The diagram shows two examples:
• Micro-duct cable systems
• Conventional loose tube cables
The Figure1 shows direct burial tubes with micro-duct cables.
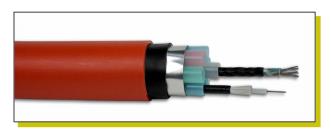
Figure1. Direct Burial Tubes
The Figure2 shows standard ducts (f.i. 40 mm HDPE) with micro-ducts and installed micro-duct cables.
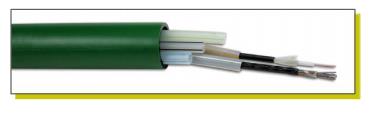
Figure2. Standard Ducts
These can blow over distances of 1km (typically). Micro ducts offer a means of deferred cable deployment.
The Figure3 shows a typical loose tube cable design. Loose tubes can be installed by blowing (as above), pulling into conventional ducts and sub-ducts; direct burial and by suspension from poles.
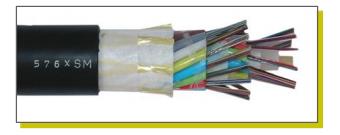
Figure3. Typical Loose Tube Cable
Related Knowledge:
Advantages of Drop Cables in FTTH
What is the technology makes FTTH broadband connections possible?



