-

- Sopto Home
-

- Special Topic
-

- FTTH Knowledge
-

- Advantages of Drop Cables in FTTH
FTTH Knowledge
- Solving the FTTH Rollout Problem in Multiple Dwelling Units
- WDM PON Introduction FAQ
- A Simple Overview of Optical Power Meter
- ODN is based on PON FTTH Optical Cable Network of the Device
- Using an OTDR to be an Expert in Fiber Link Testing
- How FTTH Broadband Works?
- Connections among Fiber Terminal Boxes & Patch Cables & Pigtails
- Easy to Install a Fiber Terminal Box
- What is Arrayed Waveguide Grating?
SOPTO Special Topic
Certificate



Guarantee
Except products belongs to Bargain Shop section, all products are warranted by SOPTO only to purchasers for resale or for use in business or original equipment manufacturer, against defects in workmanship or materials under normal use (consumables, normal tear and wear excluded) for one year after date of purchase from SOPTO, unless otherwise stated...
Return Policies
Defective products will be accepted for exchange, at our discretion, within 14 days from receipt. Buyer might be requested to return the defective products to SOPTO for verification or authorized service location, as SOPTO designated, shipping costs prepaid. .....
Applications

Sopto supply the best FTTH solutions for your network!
SOPTO Products
- Fiber Optic Transceiver Module
- High Speed Cable
- Fiber Optical Cable
- Fiber Optical Patch Cords
- Splitter CWDM DWDM
- PON Solution
- FTTH Box ODF Closure
- PCI-E Network Card
- Network Cables
- Fiber Optical Adapter
- Fiber Optical Attenuator
- Fiber Media Converter
- PDH Multiplexers
- Protocol Converter
- Digital Video Multiplexer
- Fiber Optical Tools
- Compatible
Related Products
Performance Feature
FTTH Knowledge
Recommended

Advantages of Drop Cables in FTTH
The drop cabling forms the final external link to the subscriber and runs from the last FCP to the subscriber building with a distance restricted to less than 500 meters and often much less for high density areas.
The drop cables will contain only 1 or 2 fibres for the connecting circuitry and possibly additional fibres for backup or for other network architecture reasons. The drop cable will normally provide the only link to the subscriber, with no network diversity.
For underground networks the drop cabling may be deployed within small ducts, within micro-ducts or by direct burial to achieve a single dig and install solution.
Overhead drop cables will feed from a nearby pole and terminate onto part of the building for routing to the subscriber fibre termination unit.
The above may take the form of pre-terminated or pre-connectorised cable assemblies to achieve rapid deployment and connection and to meet economic and minimal disruption demands.
Air blown cables and fibre units are able to enter through the building fabric using suitable micro-duct products and route internally within the building. This will form part of the internal cabling network with the building entry device acting as the transition point for the micro-duct (external to internal material grade).
Drop cables can be divided into 3 types:
- Direct buried cable
- Blown fibre cable
- Aerial cable
Direct buried cables are available in 2 constructions; non-metal, and with metal protection (corrugated steel).
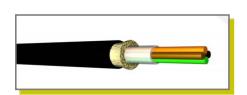
The advantage of the metal protected cables is their very high crush resistance and high-tension load. New non-metal strain relievers and protective sheets have been developed to give non-metal direct buried cables similar performance to metal protected cables. On average, non-metal cables are lower in cost.
Direct buried drop cables are available in fibre count from 1 to 12 (typical 2- 4). Direct buried cables and blown fibre cables can be pre-connectorised which gives an advantage on installation (less installation time in the home and better planning).

Direct Buried Drop Cable with Armour Protection
Blown fibre cable consists of a direct buried micro-duct (typical sizes inner tube: o.d 3, 4 and 5 mm) through which a fibre unit or micro-cable can be blown. Typically 2 to 12 fibres can be blown in this duct cable.

Air Blown Unit Drop Cable
Aerial cables are available in 3 types:
- ADSS: All Dielectric Self Supporting
- Figure 8 (cable fixed to a steel wire)
- OPGW (optical ground wire)
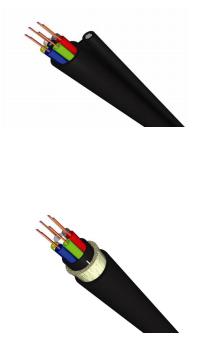
Aerial cables
Both ADSS and Figure 8 cables can be used as a drop cable for fibre to the home applications. OPGW cables are mainly used in power line connections.
ADSS cable is a non-metal reinforced cable with typical tensile load up to 5000 Newtons and fibre counts from 2 to 48.
The Figure 8 cable consists of a central tube cable fixed to a steel wire (see picture). Typical fibre counts are 2 to 48. The tensile load is typically 6000 Newtons.
Related Knowledge:
The Benefits of Fiber to the Home Broadband Connections
What is the technology makes FTTH broadband connections possible?



