-

- Sopto Home
-

- Special Topic
-

- Multiplexer Knowledge
-

- Fundamentals of Legacy SONET/SDH and Ethernet over PDH
Multiplexer Knowledge
- Why is Multiplexing Needed in Data Communication Systems?
- What is Concept of Multiplexing in Telephone System?
- What is Digital TV Frequency?
- Outlook of the WDM Networks
- DWDM Technical Overview
- CWDM Technical Overview
- How to Activate Cable Modems?
- How to Install a Fiber Optic Modem?
- How do I Choose a Best Fiber Modem?
SOPTO Special Topic
Certificate



Guarantee
Except products belongs to Bargain Shop section, all products are warranted by SOPTO only to purchasers for resale or for use in business or original equipment manufacturer, against defects in workmanship or materials under normal use (consumables, normal tear and wear excluded) for one year after date of purchase from SOPTO, unless otherwise stated...
Return Policies
Defective products will be accepted for exchange, at our discretion, within 14 days from receipt. Buyer might be requested to return the defective products to SOPTO for verification or authorized service location, as SOPTO designated, shipping costs prepaid. .....
Applications
Multiplexers can be used to connect PBX, Hot line and other devices of network from central site to user site through fiber optical cable.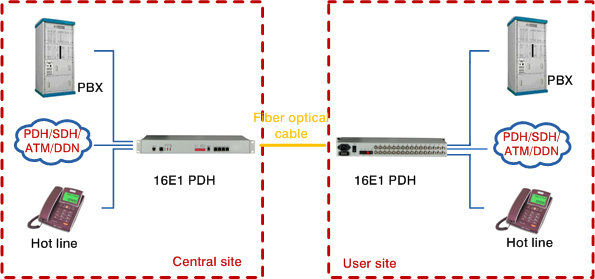
SOPTO Products
- Fiber Optic Transceiver Module
- High Speed Cable
- Fiber Optical Cable
- Fiber Optical Patch Cords
- Splitter CWDM DWDM
- PON Solution
- FTTH Box ODF Closure
- PCI-E Network Card
- Network Cables
- Fiber Optical Adapter
- Fiber Optical Attenuator
- Fiber Media Converter
- PDH Multiplexers
- Protocol Converter
- Digital Video Multiplexer
- Fiber Optical Tools
- Compatible
Related Products
Performance Feature
High integration desig
Low power consumption
Good EMC, EMI
Stable and Reliable
Multiplexer Knowledge
Recommended


Fundamentals of Legacy SONET/SDH and Ethernet over PDH
The new Ethernet over PDH over SONET/SDH (EoPoS) approach leverages, rather than deviates from, traditional transport methods. To grasp the importance of this approach, we must start with some fundamentals of legacy SONET/SDH systems.
All telecommunications equipment depends on protocol processing in silicon and software to perform the bulk of its duties. The basic protocol stack of a legacy SONET/SDH Add-Drop Multiplexer (ADM) is shown in Stack A of Figure 1. This protocol stack has been used for many years to carry the PDH Time Domain Multiplexed (TDM) services such as leased T1, E1, and DS3 lines.
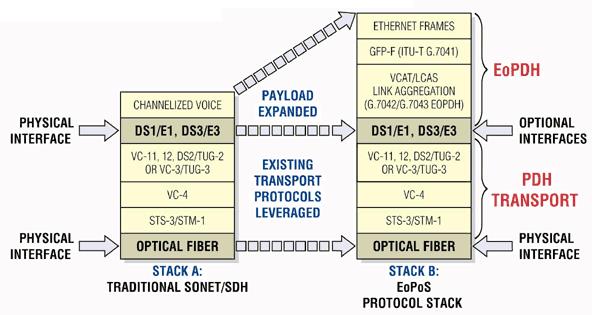
Figure1. Protocol comparison of legacy SONET/SDH with Ethernet over PDH over Sonet (EoPoS)
These PDH services—T1, E1, and DS3—are well understood, globally deployed, and trusted. Therefore, it is understandable that the ITU would adopt these PDH technologies as the transport layer for new Ethernet services. Recently, the ITU developed new recommendations for Ethernet transport over single and multiple PDH links. The applicable standards are ITU-T G.7041, G.7042, and G.7043. Collectively, these recommendations are the fundamental building blocks of Ethernet-over-PDH (EoPDH) technology. The protocol stack used in EoPDH equipment is labeled and shown in the top portion of Stack B in Figure 1.
EoPDH is a collection of technologies and new standards that allow Carriers to use extensive existing telecommunications, copper infrastructure to provide new Ethernet-centric services. EoPDH standards enable interoperability and the gradual migration of Carriers to pure Ethernet networks. The standardized technologies used in EoPDH include frame encapsulation, mapping, link aggregation, link capacity adjustment, and management messaging.
Common practices in EoPDH equipment also include: the tagging of traffic for separation into virtual networks; prioritization of user traffic; and a broad range of higher layer applications. Although EoPDH was created for point-to-point delivery of Ethernet over physical PDH tributaries, when combined with legacy SONET/SDH, EoPDH becomes an important element and cost-effective tool for Ethernet service delivery.



