-

- Sopto Home
-

- Special Topic
-

- Twinax Cable Knowledge
-

- Previous top 10 Practical Cabling Tips for Network Engineers
Twinax Cable Knowledge
- Cable Labeling as Part of Data Center Management
- How to Correctly Run cables On Servers in a Data Center?
- 4 Realities You Should Consider 10G Ethernet for Your Business
- Is it finally the end of copper?
- Why We Need Both 40G and 100G Ethernet Cable?
- What is Twisted Pair Cable?
- Benefits of Twisted Pair Cable Construction
- Why Copper Is Used in Cables?
- A Brief Look at Ethernet Cable Construction
SOPTO Special Topic
Certificate



Guarantee
Except products belongs to Bargain Shop section, all products are warranted by SOPTO only to purchasers for resale or for use in business or original equipment manufacturer, against defects in workmanship or materials under normal use (consumables, normal tear and wear excluded) for one year after date of purchase from SOPTO, unless otherwise stated...
Return Policies
Defective products will be accepted for exchange, at our discretion, within 14 days from receipt. Buyer might be requested to return the defective products to SOPTO for verification or authorized service location, as SOPTO designated, shipping costs prepaid. .....
Applications
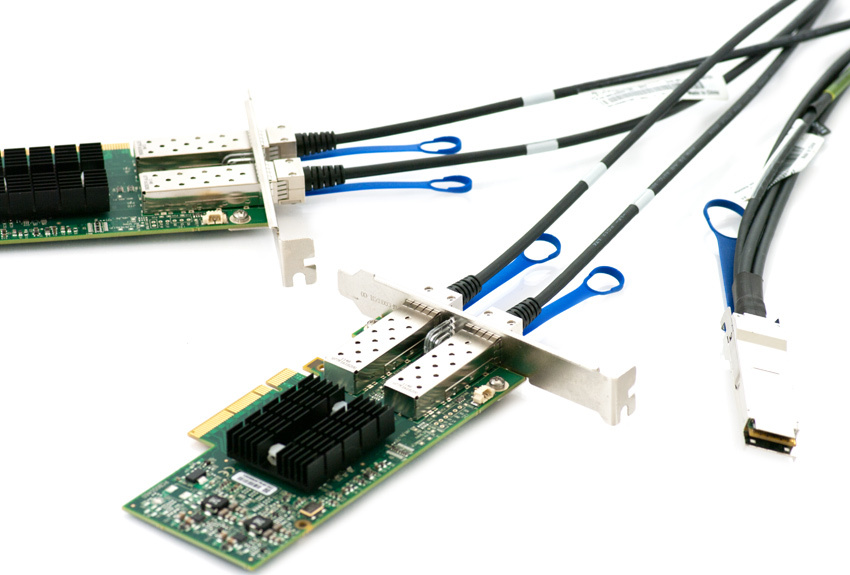 Twinax Cables are mainly used with PCI or PCI-E Card for the short distance interconnection in the server room.
Twinax Cables are mainly used with PCI or PCI-E Card for the short distance interconnection in the server room.
SOPTO Products
- Fiber Optic Transceiver Module
- High Speed Cable
- Fiber Optical Cable
- Fiber Optical Patch Cords
- Splitter CWDM DWDM
- PON Solution
- FTTH Box ODF Closure
- PCI-E Network Card
- Network Cables
- Fiber Optical Adapter
- Fiber Optical Attenuator
- Fiber Media Converter
- PDH Multiplexers
- Protocol Converter
- Digital Video Multiplexer
- Fiber Optical Tools
- Compatible
Related Products
Performance Feature
Stable Transmission Speed
Reliable Transmission
Various Length Selection
Wider Operating Temperature
Good for HPC
Good for Data Center
Twinax Cable Knowledge
Recommended


Previous top 10 Practical Cabling Tips for Network Engineers
Most Network Engineers may had forgotten or don’t know about network cabling. Sopto finds that most engineers think cable is simply plugged and played. And, mostly, that is true. In recent years, Ethernet standards and manufacturing have developed into reliable and “good enough” but the realities are still in place. Cabling needs some care and attention to detail to be reliable.
In this article, Sopto provides 10 precious practical cabling tips for engineers.
1. Cable Length Matters
The EIA/TIA standard says 100 meters is the maximum cable length. This includes patch leads. If you are using 10 meter patch leads at each end your horizontal cable run should be only 80 meters. If you have 20 meter patch leads then you can only have 60 meters in the wall.
2. Long Patch Leads can be a Bad Idea
You can go longer – it might work. It’s more likely to work if you have good quality cable and connectors and a well-executed cabling system since the electrical signal will degrade less in that environment. Cheap installs are more likely to have problems.
That’s why long patch leads can be a bad idea in some places in your office work just fine. And in other places they don’t. A 150 meter cable run probably won’t work, or worse, won’t work reliably.
3. Overloaded Cable Trays
Cable trays should not be overloaded. Suspended cable trays are mounted to something – either ceiling mounts or support from a rack underneath. If it’s too heavy, they can fall off the wall/ceiling etc. For expensive things, that will be broken.
4. Leave Space to Remove Unused Cables
Too many cables is not only a safety problem, but leads to poor operational practices when people stop removing cables from trays because it’s too hard or fear of disturbing cables.
5. Crushed Cables in overloaded cable trays.
Cables at the bottom of cable tray can be crushed by weight of cables. This especially applies to Cat6 cabling which is thicker and heavier than previous copper cabling. Cables which have been crushed will degrade signal propagation.

6. Hanging Cables will Stretch
Hanging cables within the rack means that means that gravity will induce physical stress on the copper core which will stretch and distort over time. A longer patch lead is heavier and will cause more shear stress on the cable. This will create signal degradation over time and leads to intermittent failures over time. Patch management isn’t just to keep your rack tidy; it has a mechanical purpose too.
7. Don’t pull too hard
Pulling cables can damage them by stressing the copper core. Stressing the copper core can cause stretching and thinning of the copper wire which affects the signal performance. In extreme cases it will cause unwinding of the twists in the sheath. That’s why standards specify 110Newtons as maximum draw force to be applied during installation. The cabling manufacturer should ensure that their cables are able to withstand this stress (cheap cabling is often not tested or designed; it’s just “made”).
Your cabling installer should use a force meter when pulling cable to Category 6 standards to ensure that pulling strength does not exceed to the stated maximum.
8. Electrical Conduits can’t be used for data cabling
Electrical conduits and termination boxes don’t work for Category 6 cabling because the right angle bend radii are smaller than the permitted bend radius for Cat 6 copper cable. Bend damage increases changes of cable kinking, copper core stress and leads to signal degradation.
9. Less Copper
Cheap cable has lower than standard diameter copper cores which causes signal loss and results in imperfect signal propagation. When non-standard copper cores are mated to standard cores it creates more interference because impedance mismatch causing signal reflections due to impedance mismatch. Narrow diameter cores are also physically weaker and are more likely to snap or stretch further over time thus making them more likely to fail.
10. Cheap Patch Leads
Don’t use cheap patch cords. Again, cheaper cables often don’t quite match the standard and can cause signal degradation. (Sopto’s Patch Cords are good quality) Other possibilities to reduce manufacturing costs include:
- Non pure copper cores,
- Poor quality control over twist ratios,
- Poor packaging
- Sub-standard sheathing
Because these things can all result in damaged copper cables.
For more products’ information, please contact a Sopto representative by calling 86-755-36946668, or by sending an email to info@sopto.com.