- Fiber Optic Transceiver Module
- High Speed Cable
- Fiber Optical Cable
- Fiber Optical Patch Cords
- Splitter CWDM DWDM
- PON Solution
- FTTH Box ODF Closure
- PCI-E Network Card
- Network Cables
- Fiber Optical Adapter
- Fiber Optical Attenuator
- Fiber Media Converter
- PDH Multiplexers
- Protocol Converter
- Digital Video Multiplexer
- Fiber Optical Tools
- Compatible
- Can SFP+120KM be available? ...
- Can XFP transceiver modules ...
- Is there a module which can ...
- Can different brands SFP tra...
- How long will you change you...
- The difference between DDM S...
- Comparison of EPON and GPON
- Should we use 3rd party’s ...
- How to make differences betw...
- Cisco 1000BASE-SX 850nm SFP
- How to select a DWDM XENPAK ...
- What are simplex, half duple...
- Why the delivery time of DWD...
- Which parameters should be c...
- The manufacturers of optical...
- Why some optical module is d...
- Can SFP optical module work ...
- Are all SFP optical modules ...
- how to determine whether the...
- Why HP has different models ...

How to select a DWDM XENPAK transceiver?
Reading-Guide: Most of clients didn’t sure the exact wavelength and channel for DWDM&CWDM which is the essential data for optical transceiver, for example how to verify the transmission wavelength for DWDM XENPAK.
We will introduce the distinguish between CWDM&DWDM and what is XENPAK, then a conclusion of selecting DWDM XENPAK will be brought out.
What is CWDM&DWDM?
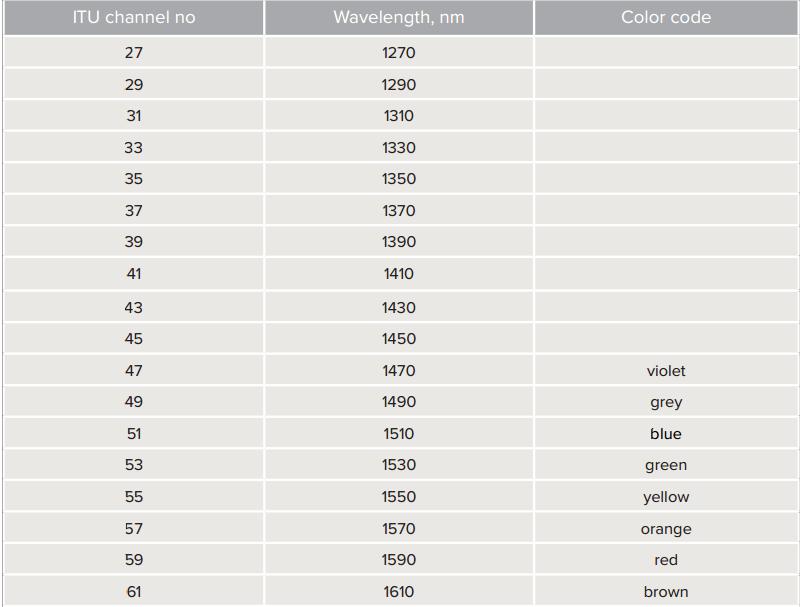
CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) Up to 18 Wavelength channels (also referred to as lambdas or colors), can be transported over a dark fiber network. Up to 8 channels can be transported over a single dark fiber strand. These wavelengths are between 1270 and 1610nm and covered by ITU standard G.694.2. Each wavelength is separated by 20nm and due to the physical properties of light, each channel cannot interfere with the next, meaning complete separation from each other. Each channel is usually transparent to the speed and type of data, meaning that any mix of SAN, WAN, Voice and Video services can be transported simultaneously over a single fiber or fiber pair.
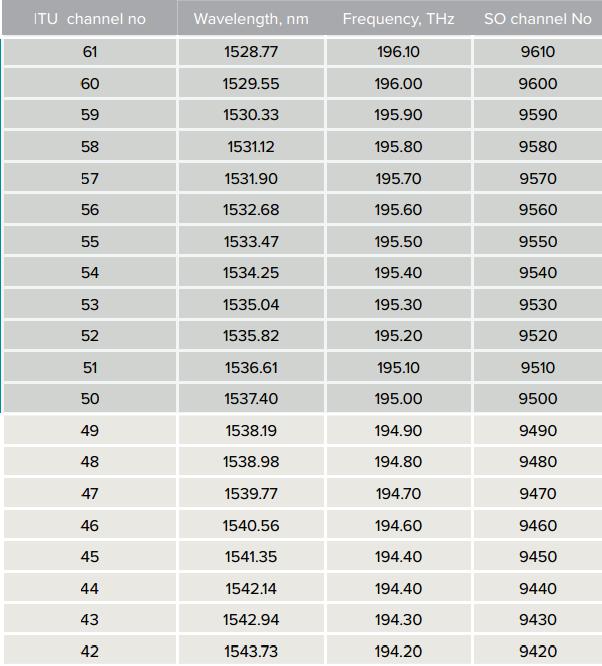
DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) 100GHz spacing (even channels) Up to 40 Wavelength channels can be transported over a dark fiber network in the so called C-Band. An additional 40 channels are available in the L-Band but these are usually not used, due to
difficulties in amplification and excessively long lead times. Networks are usually built with transceivers in the C-Band region. These wavelengths are covered by ITU G.694.1 and each wavelength is typically separated by 0.8nm or 100GHz. Each channel is usually transparent to the speed and type of data, meaning that any mix of SAN, WAN, Voice and Video services can be transported simultaneously over a single fiber or fiber pair. Apart from number of available channels DWDM has 4 additional benefits over its CWDM cousin: • Tunable transceivers are available for 10G and 100G protocols which helps with spares and logistics • DWDM wavelengths sit in a region of the fi ber that can be amplified to extend the reach of the transceiver beyond its usual stated range • It is better suited for higher speed protocols, such as 10G and even coherent 40/100G • DWDM wavelengths sit in the lowest loss region of the fiber maximising transmission distances.
DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) 50GHz spacing (Interleaver) An interleaver further expands the number of channels per fiber by multiplexing 50GHz spaced DWDM signals on to a 100GHz spaced channel plan. The 50 and 100GHz signals are commonly referred to as odd and even signals and it is these signals which are combined or interleaved together typically to move from 40 to 80 channels in the C-Band of the fiber.
Conclusion:
Distinguish between CWDM&DWDM
1, Wavelength channels: CWDM-- Up to 18 of;
DWDM(50Ghz)--40 to 80 channels in the C-Band of the fiber
DWDM(100Ghz)-- Up to 40 Wavelength channels in C-Brand
Additional 40 channels are available in the L-Band
2, Wavelength Range: CWDM--1270nm to 1610nm
DWDM--Refer to the sheet of channel and wavelength coincidence
3, Separate wavelength gap: CWDM--20nm
DWDM—0.8nm
What is XENPAK?
XENPAK is a multisource agreement (MSA), instigated by Agilent Technologies and Agere Systems, that defines a fiber-opticor wired transceiver module which conforms to the 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10GbE) standard of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.3 working group. The MSA group received input from both transceiver and equipment manufacturers during the definition process. XENPAK has been replaced by more compact devices providing the same functionality. It is the first generation of 10G SFP transceiver which is with large package format.
What is DWDM XENPAK?
The use of DWDM filter in XENPAK to transmit longer distance.
Conclusion:
How to choose DWDM XENPAK?
According to your request wavelength to sure that do you need CWDM or DWDM?
CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing)
DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing)
100GHz spacing (even channels)
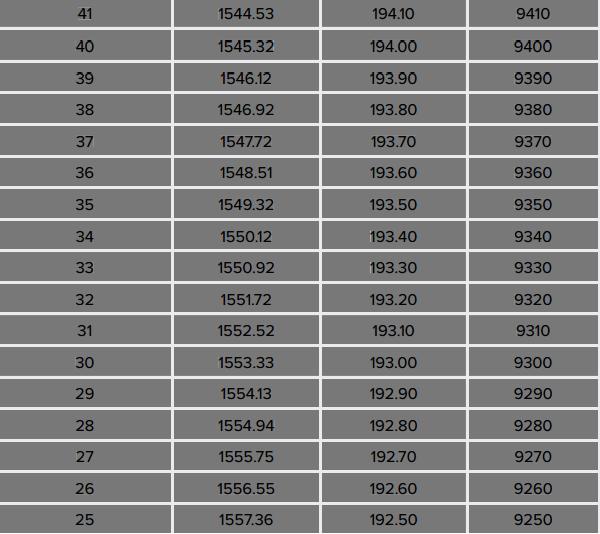
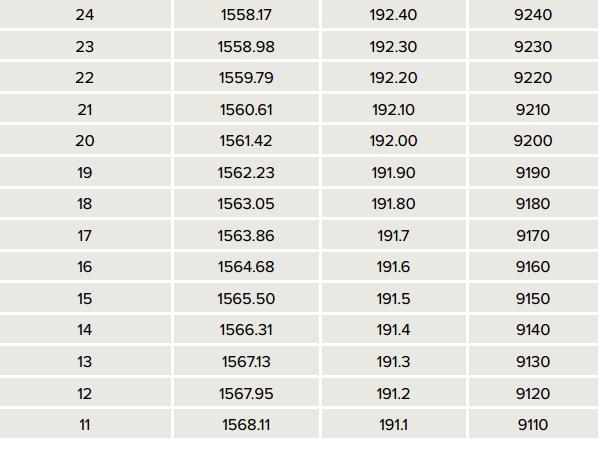
50GHz spacing channels
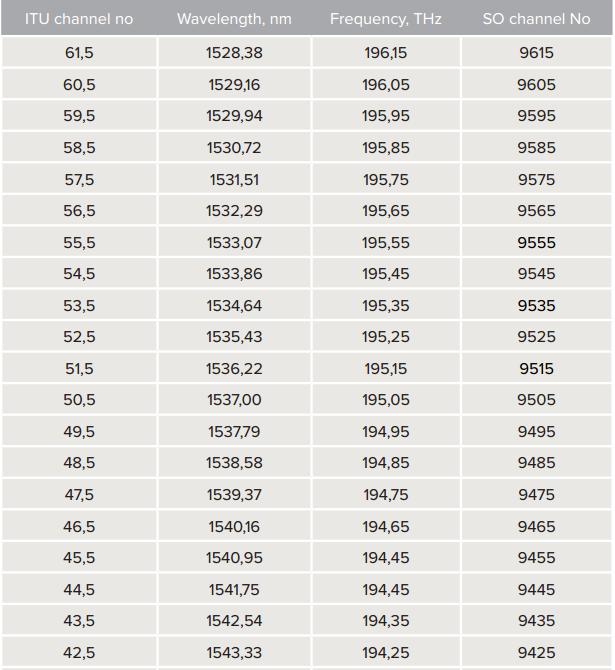
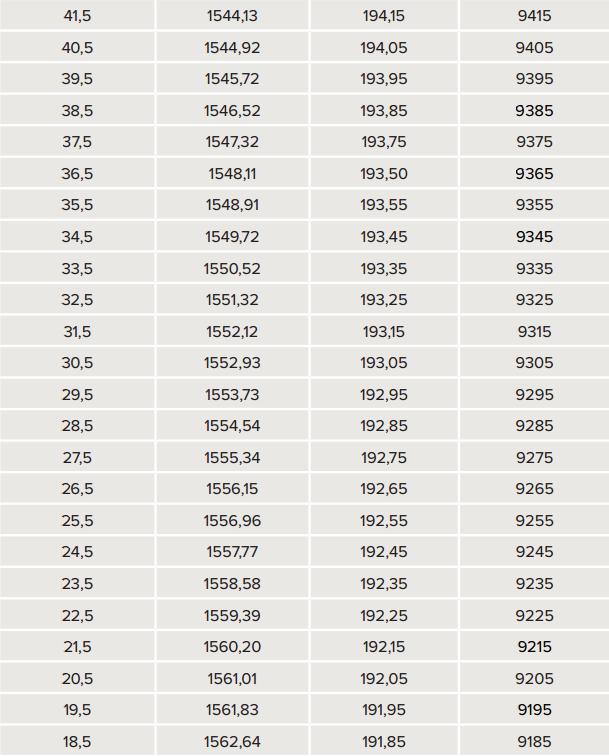
Most of requirement of DWDM XENPAK is base on 100Ghz, but less of customer need DWDM XENPAK or DWDM 10G Optical Transceiver base on 50Ghz.
Let us do a example to practice how to select a DWDM XENPAK by SOPTO’s Part Number.
SOPTO can supply both of 100Ghz and 50Ghz DWDM XENPAK and DWDM 10G transceiver, as a professional and historic producer of Fiber Optical Products such as Fiber Optical Transceiver.
SPT-KD17TG-40D
SP is for SOPTO, T is for Transceiver, KD is for DWDM XENPAK, 17 is for DWDM channel, the wavelength could be refer to the above sheet, TG is for Ethernet 10G, and 40D is for 40km with DDM function, this generation type is for 100Ghz.


