Multiplexer Knowledge
- Why is Multiplexing Needed in Data Communication Systems?
- What is Concept of Multiplexing in Telephone System?
- What is Digital TV Frequency?
- Outlook of the WDM Networks
- DWDM Technical Overview
- CWDM Technical Overview
- How to Activate Cable Modems?
- How to Install a Fiber Optic Modem?
- How do I Choose a Best Fiber Modem?
SOPTO Special Topic
Certificate



Guarantee
Except products belongs to Bargain Shop section, all products are warranted by SOPTO only to purchasers for resale or for use in business or original equipment manufacturer, against defects in workmanship or materials under normal use (consumables, normal tear and wear excluded) for one year after date of purchase from SOPTO, unless otherwise stated...
Return Policies
Applications
Multiplexers can be used to connect PBX, Hot line and other devices of network from central site to user site through fiber optical cable.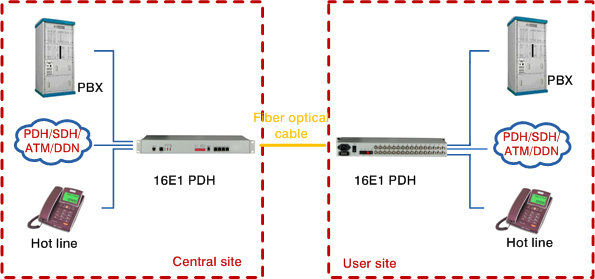
SOPTO Products
- Fiber Optic Transceiver Module
- High Speed Cable
- Fiber Optical Cable
- Fiber Optical Patch Cords
- Splitter CWDM DWDM
- PON Solution
- FTTH Box ODF Closure
- PCI-E Network Card
- Network Cables
- Fiber Optical Adapter
- Fiber Optical Attenuator
- Fiber Media Converter
- PDH Multiplexers
- Protocol Converter
- Digital Video Multiplexer
- Fiber Optical Tools
- Compatible
Related Products
Performance Feature
Recommended


- Multiplexer and Demulitplexer Based on CWDM
Before the introduction of CWDM multiplexer, it is necessary to mention the CWDM technology. Originally, the term “coarse wavelength division multiplexing” (CWDM) was fairly generic, and meant a number of different things.
- Multiplexer Used in Multiplexing
In telecommunications and computer networks, multiplexing (also called muxing) is a technique by which multiple analog message signals or digital data streams are combined into one signal more than a shared medium.
- What is Multiplexing?
Multiplexing is the technology that is able to combine multiple communication signals together in order for them to traverse an otherwise single signal communication medium simultaneously.
- What is the Advantage of the CWDM Multiplexer Module?
CWDM is a low-cost WDM transmission technology for metro access layer. Principle, CWDM may be the utilization of the optical multiplexer to different wavelengths regarding signals multiplexed with a single optical fiber for transmission
- DWDM is Also Sometimes Called Wave Division Multiplexing?
With the introduction from the fiber optic communication industry by the challenges from the growing need for bandwidth and speed requirements.
- SDH Compared To OTN
It’s no surprise that OTN has many similarities to SDH, as many of its characteristics were taken from previous technologies when SDH was defined.
- Multiplexing Basics
When you need to carve up an expensive resource (such as an active fiber route) into pieces, multiplexing is the way to go.
- SDH Frame Structure
The STM-n frame structure is best represented as a rectangle of 9 x 270xN. The 9xN first columns are the frame header and the rest of the frame is the inner structure data (including the data, indication bits, stuff bits, pointers and management).
- What is the difference between SDH and PDH?
PDH or the plesiochronous digital hierarchy is a popular technology that is widely used in the networks of telecommunication in order to transport the huge amounts of data over the digital equipment for transportation like microwave radio or fiber optic s
- PDH Network Elements
The inland management functionality enables the SDH network manager to receive information about the quality of service, the damaged elements (if there are any) and gives the manager the option to change the network configuration from a remote site.
- What are Disadvantages of PDH?
No world standard format, Plesiochronous system, i.e. signals aren’t derived from a common clock, Inability to identify individual channels in a higher order bit stream.
- Typical Interfaces of PDH Multiplexer
Typical interfaces of PDH multiplexers mainly include BNC interface, Fiber interface, RJ45 interface, RS232-C interface and RJ11 interface.
- PDH Multiplexer Common Problems and Solutions
In the project of security monitoring, most cable is laid by users, typically G652 single-mode fiber. Because the scope of the system is not large generally, the link loss is enough even to use the standard equipment (≤20km).
- T1 Frame and E1 Frame of PDH
Until the late 1950s the telephone system consisted almost entirely of analogue transmission lines. Trunk lines between exchanges carried multiple voice channels simultaneously using frequency division multiplexing (FDM).
- Origins of SONET
SONET was created by the ECSA (Exchange Carriers Standard Association) to allow a standardized and normalized connection between fibre optic systems, even though different manufacturers had designed them.
- Plesiochronous Transmission
Digital data and voice transmission is based on a 2.048Mbit/s bearer consisting of 30 time division multiplexed (TDM) voice channels, each running at 64Kbps (known as E1 and described by the CCITT G.703 specification).
- Tributary of Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy
As bandwidth demand grew the technology called Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy (PDH) was developed by ITU-T G.702, whereby the basic primary multiplexer 2.048Mb/s trunks were joined together by adding bits (bit stuffing) which synchronised the trunks at
- Optical Transport Network has Taken Hold as the Protocol of Choi
Transport protocols have evolved over a very long time, and each generation has inherited many attributes and behaviors from its predecessors. The dominant protocol in the transport network over much of the past two decades has been the synchronous digita
- Future of Optical Transport Network
The deployment of OTN has primarily been for the transport of SDH and 10GE signals. Many recent changes to the OTN standards have broadened functionality to support 40- and 100-Gbit/s operation and added better capability for Gigabit Ethernet and other pr
- Features and advantages of SDH/SONET
Today's carrier backbone networks are supported by synchronous optical network (SONET) and synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) transmission technologies. SONET is the standard used in the United States and SDH is the standard used outside the United State





